Toxic haze chokes Indian capital
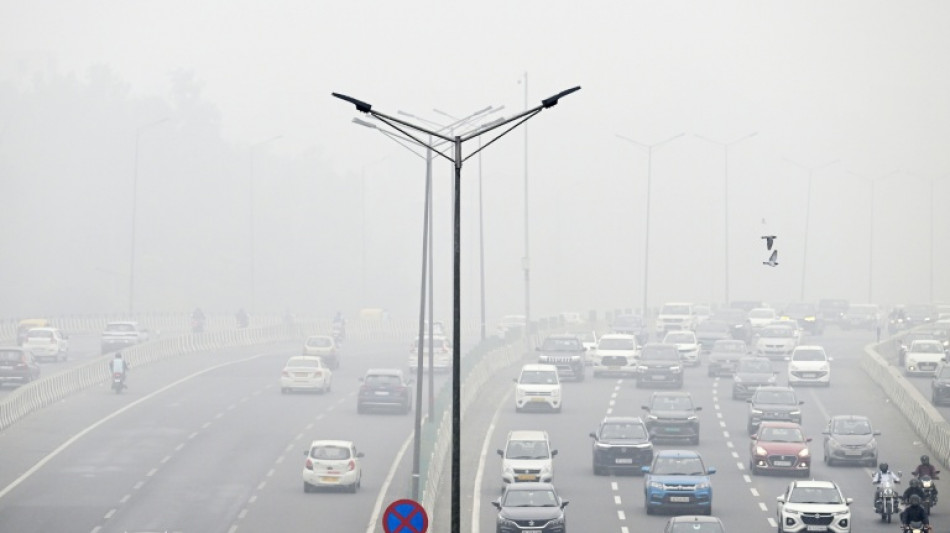
India's capital New Delhi was shrouded in a thick, toxic haze on Monday as air pollution levels soared to more than 16 times the World Health Organization’s recommended daily maximum.
New Delhi and its sprawling metropolitan region -- home to more than 30 million people -- are regularly ranked among the world's most polluted capitals, with acrid smog blanketing the skyline each winter.
Cooler air traps pollutants close to the ground, creating a deadly mix of emissions from crop burning, factories and heavy traffic.
But pollution has also spiked due to days of fireworks set off to mark Diwali, the major Hindu festival of lights, which culminates on Monday night.
The Supreme Court relaxed this month a blanket ban on fireworks over Diwali to allow the use of the less-polluting "green firecrackers" -- designed to emit fewer particulates.
The ban was widely ignored in past years.
On Monday, levels of PM2.5 -- cancer-causing microparticles small enough to enter the bloodstream -- hit 248 micrograms per cubic metre in parts of the city, according to monitoring organisation IQAir.
The government's Commission of Air Quality Management said air quality is expected to further deteriorate in the coming days.
It also implemented a set of measures to curb pollution levels, including asking authorities to ensure uninterrupted power supply to reduce the use of diesel generators.
City authorities have also said they will trial cloud seeding by aeroplanes for the first time over Delhi this month, the practice of firing salt or other chemicals into clouds to induce rain to clear the air.
"We've already got everything we need to do the cloud seeding", Delhi Environment Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa told reporters this month, saying flight trials and pilot training had been completed.
A study in The Lancet Planetary Health last year estimated 3.8 million deaths in India between 2009 and 2019 were linked to air pollution.
The UN children's agency warns that polluted air puts children at heightened risk of acute respiratory infections.
F.Morgan--VC